How piezoelectric accelerometers work: principles and designs
All piezoelectric accelerometers operate on the same basic principle: a seismic mass applies force to a piezoelectric material, typically a crystal or ceramic. The resulting stress generates an electrical charge proportional to the applied force. This force is influenced by the size of the mass and the level of acceleration. Additionally, the output charge depends on the amount of piezoelectric material used, meaning that accelerometers with higher sensitivity are often larger and heavier.
Three primary accelerometer designs
Image
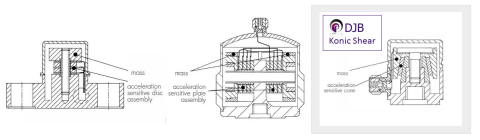
The construction of a Konic™ Shear accelerometer
Latest news and events



